Advanced manufacturing: what is it?
Advanced manufacturing makes use of disruptive technologies and materials to
improve the efficiency, productivity, and quality. Here’s how.
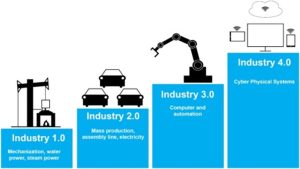
The emergence of advanced manufacturing is a natural evolution of the industry, driven by a shift in workforce dynamics, rapid technological advancements, and a pressing need for more resilient supply chains in the face of global disruptions. This new, transformative landscape offers opportunities but also poses challenges, with several implications for workers, businesses and even for society at large.
What is Advanced Manufacturing?
Advanced Manufacturing is the term used to describe companies that use innovative technologies and processes – like automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, or virtual reality – to increase efficiency, productivity, and quality. It is nothing more than the latest generation of industrial processes that incorporate innovative and oftentimes disruptive technologies and materials.
Source: ScienceDirect
It is sometimes pointed out as one of the crucial elements of Industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and represents a true paradigm shift in manufacturing, where physical and digital technologies converge to create “smart factories” and interconnected production systems.
What are the benefits of Advanced Manufacturing vs Traditional Manufacturing?
There are several reasons why Advanced Manufacturing is changing manufacturing environments:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Advanced manufacturing technologies optimise processes, reduce lead times, and minimise waste, leading to higher productivity and cost savings.
- Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency: Precision control, predictive maintenance, automated quality assurance, and others, result in higher-quality products with improved performance and greater reliability.
- More Customisation: Advanced Manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and configurable production lines, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changing market demands.
- Sustainability: Advanced manufacturing techniques can help minimise waste, energy consumption, and carbon emissions.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Advanced manufacturing technologies reduce dependence on traditional suppliers and geographically concentrated production, help minimising disruptions caused by part shortages or equipment failures, and to respond effectively to natural disasters or geopolitical events.
- Workforce Development: new technologies create new opportunities for skill development, training, and career advancement, and allow for new career paths in areas like AI integration, programming, data analysis, and process optimisation.
Examples of Advanced Manufacturing technologies
Advanced Manufacturing makes use of very widespread group of technologies – let’s call them the usual suspects: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data Analytics, and Cloud Computing .
Who’s who in Advanced Manufacturing

Source: CB Insights
However, there are many other innovative and disruptive technologies continuously improve, optimise, and enhance traditional manufacturing, into the more efficient advanced manufacturing.
Automation and Robotics
Advanced Manufacturing uses very advanced automation and robotics to achieve, for example, high-degree precision. These technologies can be used for a variety of tasks from assembly and welding to more precise tasks such as quality inspection.
Tesla’s advanced manufacturing facilities heavily rely on automation and robotics for tasks such as assembly, welding, and quality inspection in their electric vehicle production. Automation allows Tesla to achieve high precision, increase production efficiency, and maintain consistent quality across their vehicles, contributing to their success in the automotive industry.
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3-D printing, includes methods like powder-bed laser printing and fused deposition modelling to create three dimensional models via layer deposition from a digital design and using one continuous material. It differs from the traditional subtractive manufacturing, which involves cutting away material from solid blocks of different materials.
GE Aviation utilizes additive manufacturing technologies to produce complex components for aircraft engines, such as fuel nozzles and turbine blades. Additive manufacturing enables GE to create lightweight, durable parts with intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods. This technology enhances engine performance, reduces fuel consumption, and lowers maintenance costs for airlines.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology allows for the manipulation of materials at an atomic or molecular level, which in turn allows for the creation of advanced materials with very specific characteristics. These novel or improved materials can help develop new techniques and methods in advanced manufacturing.
Lockheed Martin incorporates nanotechnology into the development of for aerospace and defense applications. By manipulating materials at the nanoscale, Lockheed Martin can create lightweight yet strong materials for aircraft, spacecraft, and military equipment. Nanotechnology also enables the production of coatings with special properties, such as stealth capabilities or resistance to corrosion, enhancing the performance and durability of their products.
Advanced/Composite Materials
Advanced or composite materials are precise blends of different materials that acquire very specific characteristics, and are used in very specific situations, such as biomaterials, nanomaterials, high-strength alloys, or other composites.
Boeing utilizes advanced composite materials in the manufacturing of commercial aircraft, including the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. By incorporating composite materials such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), Boeing is able to reduce the weight of aircraft structures while maintaining strength and durability. This results in fuel savings for airlines, increased range, and improved passenger comfort.
Laser Machining and Laser Welding
Cutting and welding materials with a highly focused laser allows for increased precision, reduced distortion, remote operations, automation and also allows for the manipulation of a wide range of materials.
Trumpf is a leading manufacturer of laser cutting and welding systems used in various industries including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Their laser technology allows for precise cutting and welding of a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This enables manufacturers to achieve high-quality results with minimal distortion, increased efficiency, and greater flexibility in production processes.
Digital Twin
Digital twin technology enables the creation of a virtual replica or simulation – ergo, a digital twin – of a physical object, process, or system. Digital twins are used for virtual prototyping, design optimisation, remote control and testing, life cycle assessment, and others, even before the physical object even exists.
In Healthcare, digital twin technology can be applied to create virtual replicas of individual patients or specific organs. It allows healthcare professionals to simulate various medical scenarios, such as surgeries or treatment plans, before performing them on the actual patient. By analyzing the digital twin’s data and running simulations, doctors can personalize treatment strategies, optimize surgical procedures, and predict potential outcomes with greater accuracy.
In Automative Industry, Ford utilizes digital twins to design and test new vehicle models virtually before physical prototypes are built. This approach enables Ford to iterate quickly, reduce development costs, and ensure that their vehicles meet safety and performance standards before production begins.
Network and IT Integration
Connecting the various components, systems, and processes within a manufacturing environment through digital networks and information technology infrastructures enables real-time communication, and data exchange, as well as coordination throughout all the stages of the manufacturing cycle, providing instant notification when an issue arises.
A use case to this solution would be a manufacturing company implementing network and IT integration to streamline its supply chain operations. By connecting its ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system with suppliers’ systems through digital networks, the company can automate order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking. This integration improves visibility, communication, and coordination across the supply chain, reducing lead times and inventory holding costs.
Or you can be a multinational corporation who implements network and IT integration to enhance collaboration among its global workforce. By deploying cloud-based collaboration tools, such as video conferencing, document sharing, and project management platforms, employees can seamlessly communicate and collaborate across different offices and time zones. This integration improves productivity, fosters innovation, and strengthens teamwork across the organization.
IIoT
IIoT stands for Industrial Internet of Things, and just like the name suggests is the application of IoT technology to an industrial context. This means a network of interconnected devices, sensors, machines, and systems within industrial environments that communicate and share data to optimise processes.
One real example is the implementation of an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) system in a factory setting. In this scenario, various machines, sensors, and devices within the manufacturing environment are connected through a digital network. These interconnected devices collect and exchange data in real-time, enabling seamless communication and coordination throughout the production process.
By leveraging network and IT integration, manufacturers gain insights into their operations, improve decision-making, and enhance overall productivity. This results in reduced costs, improved quality control, and increased competitiveness in the market.
Toyota Motor Corporation has implemented network and IT integration extensively in its manufacturing processes. The company uses sensors and data analytics to optimize production lines, improve efficiency, and ensure quality control in its automotive manufacturing plants worldwide. Boeing, the aerospace giant, utilizes network and IT integration in its aircraft manufacturing facilities. The company employs sensors and data analytics to monitor and optimize production processes, ensuring precision and efficiency in the assembly of aircraft components.
Solving Industry Challenges with Diverse Technologies
The truth is most industries can benefit from Advanced Manufacturing – who doesn’t like manufacturing optimisation, increased efficiency, enhanced product quality, and so on? – but certain industries are currently leading the charge in adopting advanced manufacturing technologies. For example:
- Aerospace: uses additive manufacturing for lightweight parts, robotics for precise assembly, composite and advanced materials for durability and strength, laser technologies for high-precision welds, and virtual twin technology for virtual testing of aircrafts before construction.
- Automotive: this industry uses robotics for welding and painting, automation for efficient assembly lines, AI for design and development, and Big Data analytics for process optimisation.
- Medical devices: the medical field leverages additive manufacturing to create prosthetics and implants, nanotechnology for innovative devices, or advanced materials for improved biocompatible implants, prosthetics, and devices.
- Energy: the energy sector employs advanced robotics for hazardous or remote tasks in power plants, additive manufacturing for wind turbine components, AI for power-grid optimisation, and digital twin technology to simulate and optimise operations.
- Chemicals & Materials: this industry relies on automation for precise control of complex processes, on sensor networks for real-time data for monitoring and optimising production, and on Big Data to aid in identifying trends, improving efficiency, and developing new materials.
There are, of course, a million other ways the many different sectors and industries use – to larger or lesser scale – advanced manufacturing and advanced manufacturing technologies, but we’d be here for eons. In fact, we’d need to keep updating this information, as every day there are new, innovative applications of these technologies in the manufacturing industry.
Streamline your manufacturing operations with the right Partner!
Whether you are looking to develop custom industrial software solutions, to integrate emerging digital technologies in your business’ legacy systems, to leverage machine learning algorithms, or just about anything pertaining to the tech side of advanced manufacturing, Near Partner is here for you and your business. Take a look at the Nearshore Solutions we offer or just get in touch if you are unsure of how we can help your business. Let’s create something together!





